
- IRRIGATION
- CROP MANAGEMENT
- BLUEBERRY
- ARTICLE
Optimized: Berry Irrigation in Morocco
A leading Moroccan berry grower cut water use by 16% using climate data and ETo-based irrigation....
04.02.2025 | 3 min read
Data is measurable information. In farming, data can range from straightforward metrics like rainfall amounts to more dynamic indicators like temperature fluctuations throughout the day. By using data, growers can make informed decisions on water usage, fertilizer needs, pest control, and other critical factors that impact crop health and yield.
Data can help to unlock crop growth and production as a single factor can limit crop growth and production even when ALL the other factors are perfect.

In agriculture, data enables smarter, fact-based decisions, eliminating guesswork. It reveals patterns in water usage, crop health, and local climate conditions. For example, in arid regions, data can help optimize irrigation schedules, reducing water waste while maintaining crop health.
Jim Barksdale, former CEO of Netscape.
In protected cultivation, such as greenhouses and tunnels where crops are grown, data plays a crucial role in optimizing growth conditions. By using real-time data from sensors that measure temperature, humidity and light, growers can fine-tune the environment to ensure plants receive exactly what they need at each stage of growth.
For example, in greenhouses, monitoring temperature and humidity helps maintain the ideal climate for crops, while automating irrigation based on soil moisture and substrate data ensures precise water use, avoiding over- or under-watering.
Data can help to optimize key farming practices:
Irrigation: Deliver precise water amounts, conserving resources.
Pest and Disease Management: Prevent outbreaks based on climate data.
Yield Prediction: More accurately forecast and plan for harvest.
Risk Management: Respond rapidly and proactively with real-time alerts around your climate conditions.
Harvest Timing: Better plan for resources like labour needs.
Operational Efficiency and Sustainability: Visualize trends, automate tasks, graphs and reports saving time and reducing costs. Reduce waste by optimizing inputs like water and fertilizers.
While intuition and past experiences are valuable, using data can significantly enhance your decision-making process. Data helps you identify patterns and insights, enabling you to make strategic choices that improve efficiency and productivity.
Data-Driven: Decisions are based solely on data.
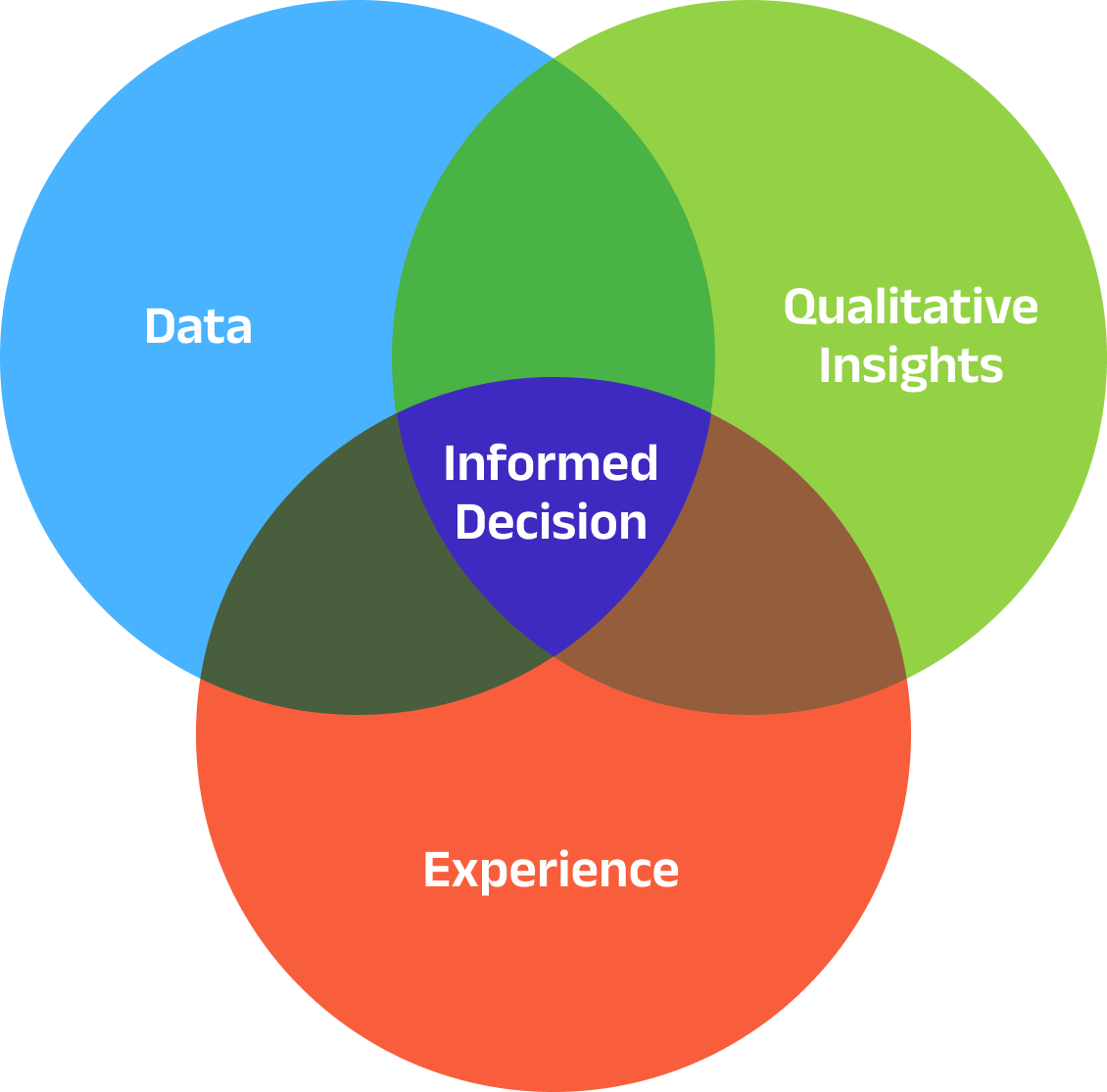
Data-Informed: Data is one of several inputs, including experience and intuition, that guide decisions.
Data (quantitative insights, e.g., microclimate data, experiment results).
Qualitative insights (e.g., customer feedback, stakeholders, changes in the market, new varieties).
Experience (aka “intuition”), which results from experience, knowledge and immersing yourself in your market and the growing environment context.
Integrating data with your expertise can result in more robust and impactful results. Enhancing data literacy is essential for achieving success with digital agronomy solutions.
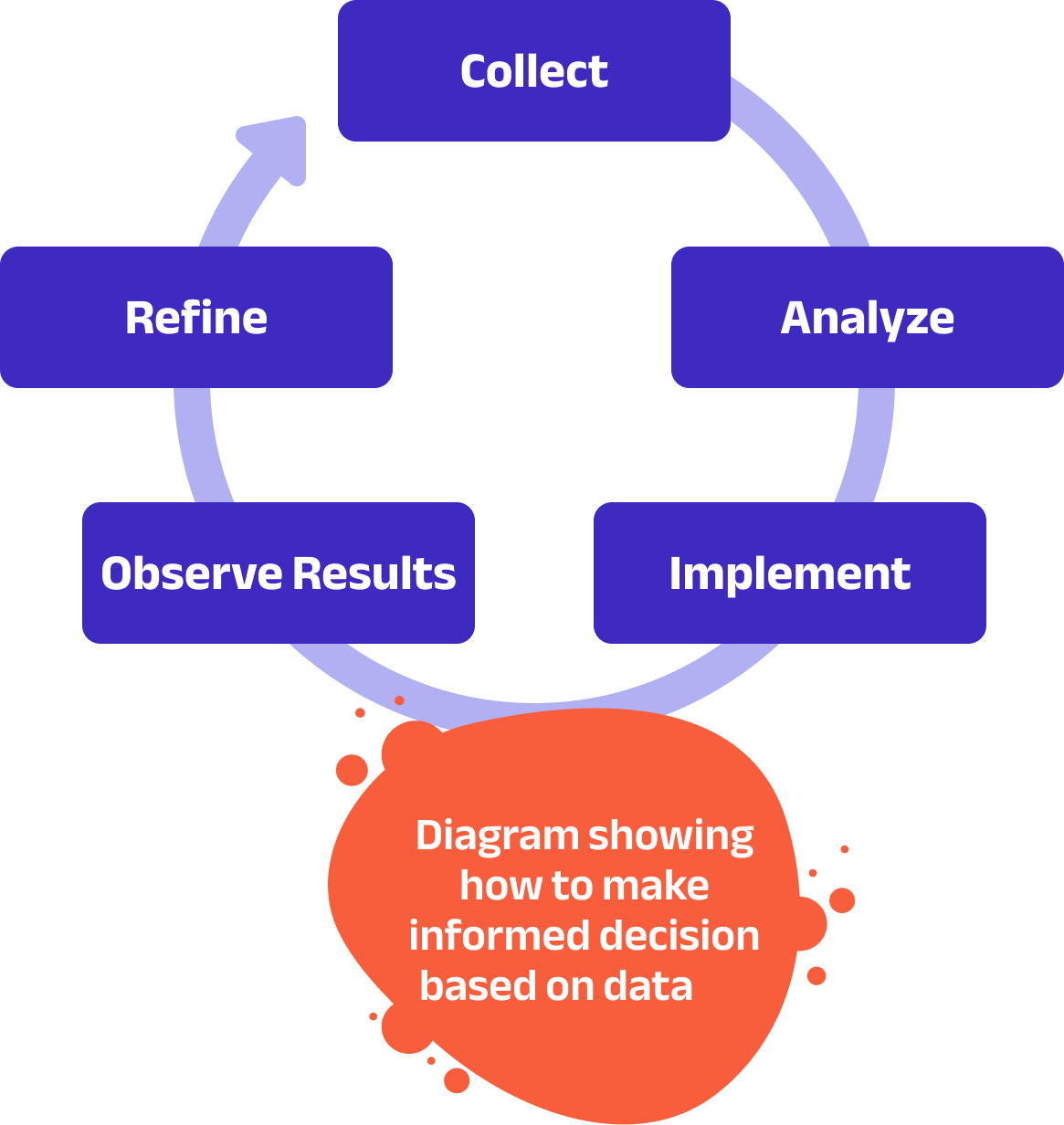
Define objectives and outcomes: get clarity on your needs and what you want to achieve
Collect it: Use sensors and other technology to gather information about your climate, weather, and crops.
Analyze the data: Look at trends and patterns to understand what’s happening on your farm.
Make informed decisions: Use your data insights to decide how much water, fertilizer, or pesticides to use.
Implement changes: Adjust your farming practices based on your decisions.
Observe and refine: Keep an eye on how your changes affect your crops and make adjustments as needed.
Situation: For instance, imagine you're growing berries. You notice your water usage is high, yet your yields aren't improving.
Collect data: The grower can leverage various data such as climate, irrigation, substrate, alongside forecasted water demand models to determine the optimal water and nutrient requirements of their crops.
Analyze the data: The grower reviews the previous day's irrigation events, including climate data (temperature, VPD, radiation), drip and drain metrics, and substrate sensor data (VWC, EC), to assess the irrigation plan's success and make adjustments for the current day.

FarmRoad dashboard displaying forecasted climate and irrigation data for informed decision-making
Decision: After review, the grower can decide how the irrigation volumes and times should be adjusted based on the forecasted water demand model for the day
Observe and Refine: Real-time monitoring of drip and drain data, along with substrate VWC and EC, enables growers to assess and adjust their irrigation plans effectively.
This approach promotes efficient water use, resulting in healthier plants, higher yields, and lower costs by preventing over-irrigation and related issues.
If you want to learn more how to use data insights to improve irrigation, check out our blog ‘An Introduction to Irrigation Using Data Insights.’
Get the full guide, complete with a checklist on using data to make informed crop management decisions.


A leading Moroccan berry grower cut water use by 16% using climate data and ETo-based irrigation....

ETo forecasting is a simple but powerful tool for optimizing irrigation every day, in every season....

See the strategy behind evapotranspiration-based irrigation planning that helped a greenhouse...

Learn how six key weather data points can help you make smarter irrigation decisions, conserve...

A smart approach to water management is key to helping growers tackle water scarcity and climate...

Uncover the vital role of drip and drain monitoring in optimizing drip irrigation farming.

Explore how protected cropping growers can use data insights to drive smart irrigation practices.
.png)
Learn how Khawla Derstaouieh embraces digital agronomy to optimize irrigation, track pests, and...

Heatflation is rising food prices caused by extreme heat from climate change. How can protected...
Champions of crop management.
Giving commercial growers the power to make better crop management decisions and optimize crop outcomes.
Solutions
Customers
©2025 WayBeyond. All Rights Reserved.